History
The operations on low-temperature spectroscopy of molecular crystals initiated at the end of 20 years ÕÕ of century by the academician I.V.Îbreimov, have reduced in necessity of making of specialized apparatus for these purposes (cryostats). Under the initiative A. F. Prihot'ko in Institute of physics AS of USSR in 40-50 y.y. the cryogenic laboratory was up second in Ukraine and third in the Soviet Union which long time after renovation and expansion formed the basis for low-temperature operations of a series of scientific organizations of Kiev. It is necessary to mark, that conventional to usage at researches in that time there were glass or quartz Dewar vacuum flasks executing a role of cryostats.
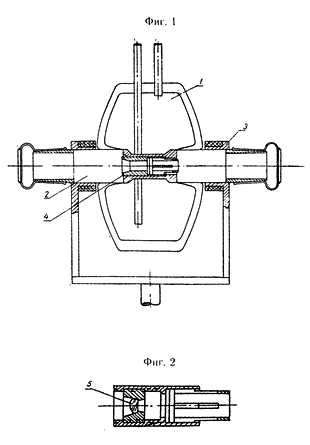
The first cryostats, with which worked of physicsians, were glass with a series of deficiencies: - they were friable accident-sensitive in maintenance, could work only with fluid(liquid) nitrogen. Therefore it was necessary to create the type of cryostats, free from the enumerated deficiencies and capable to work safely with different cryoagents. In 1949 the attempt of substitution glass exploratory dewar on metal was realized. The first mention of application of such cryostat is discovered in paper Îbreimov I.V.. and Prihot'ko A.F. In the anniversary receiving tank devoted 70-annivesary of À.I.Ioffe. 1950 y., in which the nitrogen metal cryostat with a built-in Jamen interferometer is described. The first invention on „ the Device for low-temperature optical researches ” was formed in 19.05.1950 y. by Medvedev V.s. and Broude V.L.(a. i.USSR¹102322 is produced by the Ministry of a defensive industry 25.04.1956 y.). In it the authors have offered the device for the low-temperature spectral analysis which has been carried out as the employee for a location of a dish with analyzable substance of a metal tube, supplied on test leadss by ground-in flanges with windows from a transparent material for a given site of a spectrum, and the concluded mid-range in a metal vessel, in which brings refrigerant, for example, liquid air. Schematically aspect of the device is exhibited on a fig. 1, cuvetteholder - on a fig. 2.
For incarnation of ideas of the physicians-experimenters in a metal construction on mission À.F. Prihot'ko in experimental industrial workshop IoP of AS of USSR the engineering department was set up, which designers L.I.Borodyna, Rjabchuk, Brazhkin were engaged in development of a construction of cryostats from 1954 till 1968. The customers of cryostats were such of scientist - physicianss as À.F. Prihot'ko, V.L.Broude, V.S. Medvedev, M.S. Brodyn, Î.L.Fialkovskya, L.S.Êremenchugsky and others.
The metal cryostats, developed in that time, were of different types: nitrogen, nitrogen-paraffin, hydrogenous and helium.
The majority of cryostats were not folding, though met sometimes with folding flanges in upper or bottom of a cryostat. As a rule, the cryostats had the cylindrical shape. Only few were spherical or hemispherical. The trailing-edges of cryostats also were different, depending on assignments. For exterior electromagnets the trailing-edges had the flat shape. Some cryostats had below metal body crossing to a glass trailing-edge.
Further (1951) the invention of V.S. Medvedev has followed. , where on any sketches it is possible to judge, what is it there was a cryostat with a cool finger (apparently, cooled bolometer). Invention was obtained in 1956 and was enclosed.
The vacuum cocks in the first cryostats had tapered ground-in microsections. The level gauges of cryoagent were flash float. Slide gates of sluice chamber- eccentric type.
The external windows of cryostats were made on metal microsections, on rubber seals and on glue.
Overall dimensions of cryostats - most different: external diameter from 100 up to 200 mm, height from 500 mm and more than 1 m.
In 1956 y. in a journal « Instruments and technique of experiment » (ITE) (date of feeding of paper 24.05.1956 ) the cryostat for optical measurings is described at temperature of liquid hydrogen (V.L. Broude, V.S.Medvedev, V.P.Babenko).
In the same year in a journal ITE ¹3 (authors M.S.Brodyn, V.S.Medvedev, À.F.prihot'ko) the metal cryostat for a research with the help of an interferometer such as Zhamen of a dispersion of a light in chips is described at temperature of liquid hydrogen. An interferometer with a crystall places in cryostat work chamber and cools by a hydrogen vapor. Series of solutions here is described which have found the application in further designs: window leads, nitrogen shield cooled carbon socket (cartridge). Temperature of liquid hydrogen - 20 K, cryoagent consumption 0,5 ë/hours. Besides it was the first cryostat of a folding type.
In 1957 the hydrogenous cryostat with cuvetteholder on a rod and mechanism of rotational displacement of a sample (journal « Optics and spectroscopy » .v.2. issue.3. the authors: V.L.Broude, V.S.Medvedev and À.F.Prihot'ko) was used.
In 1959 in ITE ¹ 1 in paper « the Methods and instrumentation of low-temperature optical and spectral researches » (V.P.Babenko, V.L.Broude, V.S.Medvedev and À.F.Prihot'ko) are described:
². A faultless vacuum seal of glass and quartz windows (Fig. 5);
²². The schemas(circuit) of hydrogenous and helium cryostats; ²² a series of insertions in cryostats, which allow: to conduct spectral researches of chips in a polarized light; spectral researches of substances in requirements of multifold squeezing at pressure of gas up to 200 àòì.; measuring of a spectral distribution law of a photocurrent, including in requirements multifold or lateral contraction of a chip.
Then the cryostats for: studies of phase changes with the device of crystalline modification, for a research have appeared at multifold squeezing at pressure of gas up to 200 àòì, for spectral and electrophase researches in requirements of a lateral contraction. In their construction were already utillized: an air lock, liquid level indicator of a flash float type.
Since 1963 have refused an nitrogen jacket, prolongation(continuation) of an nitrogen can became the copper shield cooled by nitrogen. The windows on the nitrogenc shield, as a rule, missed, but sometimes staked diaphragms and only much later (approximately in 1968) on the nitrogenshield the windows have appeared.
The helium cans of cryostats had an interior beaker, which allowed to arrange a sample in vapours or fluid and even to control its temperature. In some of a cryostat (1967) the sample seated under a helium can in vacuo on cold finger. With the help of a heater it was possible to control its temperature. Besides were attempts to control temperature with the help of a gas stream. For this purpose in a place of disposition of a sample the feeding of gaseous cryoagent is carried out.
The helium windows in 50 - 60 years in basic were made on tapered swages with capsulation on rubber gaskets, and only later, at the end of 60 windows began to glue on epoxy resin
.In connection with propagation of necessities of the experimenters in cryostats which are taking into account specificity of their researches, and providing a thermal control of samples in a range 4 - 300 K in 1965 in Institute under the initiative À.F.Prihot'ko the special design-engineering group under V.S.Medvedev management was organized. Its task was a further development of cryostats for physical experiments both for our Institute, and for other institutes of an Academy of sciences. In composition of group in the beginning have come: the designers Bondarenko Å.M., Fedorovich Î.L., mechanicses Vlaznev Î.I., physician - experimenter Apostolov À.I.. By a year later mechanicses-designer dhas joined of group.
At the end of 60 years in group also worked: the designers Podolich V.B. , Tchmul À.G., mechanicses Gohman V.H.
It is necessary to mark, that creative union of two talented people: the engineer - physicians - inventor Medvedev V.S. and mechanics - designer- specialist in cryogenic fiel Ermakov V.M. has yielded a bull push to further development of cryogenic instrument making in IP of NAS of Ukraine.
In the begining of 70 years to activity of group the electronic engineer V.V.Sergienko has connected. The group has gained in Institute the status of structural subdividing - department and in it were actively ordered works on such directions:
- Design of constructions of cryostats, their separate clusters, breadboarding and tests. This direction of cryogenic researches has headed by V.M.Ermakov;
- Solution of specific designer problems for needs of physical experiment. This group has headed A.G.Tchmul;
- Design of devices of automatic control of temperature has occupied V.V.Sergienko, then P.V.Vodolazsky.
So, in a journal ITE ¹5 in 1973 was described cryochamber, permitting to conduct roentgenodifractomic researches of polycrystallic samples and sections of single crystals in an interval of temperatures 4,2 - 300 K at stability of given temperature ± 0,05°.
The cool-off and thermostatic control of a sample is carried out in a work chamber by a stream of gaseous He, having temperature, close to given. The application of this way has allowed to construct a rather prime system of an automatic stability control of temperature in any point of a temperature range 4,2 - 300 K, based on regulating of a mass of a stream He, to provide high profitability of a gear and it's good service performance.
By apogee of creative and scientific activity of V.S.Medvedev, was author invention of USSR ¹436334, fed and made out in 1974 by collective of the authors headed by V.S.Medvedev (organization - applicant: Iinstitute of physics of AS USSR). This invention was by revolutionary work, opening a road to making precision costeffective temperature-controlled cryosystem. As a matter of fact it was the licensed method of high-precision temperature control in cryostats.
The first temperature controllers represented a gang of gears, serially emitted by the Soviet industry, with including in it self-maintainedly designed analog multiplier of a signal of disbalance between given and setted-up temperature. So, for example, as a setting unit have used depending on a type of an elected temperature detector -thermoresistor either thermoelectric couple the bridge of resistances or comparator of voltages, accordingly. For a recording device was a recorder. Even despite of this deficiency the received technical characteristics of cryosystems were so high (stabilization of temperature not worse ±0,1Ê, the cryoagent consumption of liquidòà is no more 0,12 ltr/hours), that they called broad interest the scientists - experimenters not only Soviet Union, but also states of Union of economic mutual aid. By the first foreign customers - were the scientists from Institute of physics of AS of Chechoslovakia (Prague) and Humboldt University(Berlin, GDR).
The received success was necessary to anchor by elimination of a gang of final control devices creating problem by delivering and complete set of workpieces. Therefore there was a problem of making of a temperature controller, capable self-maintainedly to control of temperature with a split-hair accuracy. The engineer - physisist- specilized in electronic V.V.Safronov has undertaken its solution., joined in Medvedev's department in 1977. To him for the aid the engineer - expert in digital technique Dotsenko K.A.has came. The problem of creating of final control devices for regulating gas streams and uniform construction for a temperature controller was decided by the designers group of A.G.Tchmul.
The work on creation of a temperature controller was completed by deriving in 1987-1990 y.y. of author inventions of USSR ¹ 1315960 and ¹ 1594504, due to which implantation designed cryosystem have received a compact aspect: instead of a gang of a series of industrial gears one temperature controller was used, providing high stability of temperature and its indication in service . In parallel with this activity the operations on refinement of constructions as cryostats, and accesssories to them (sluice gates, manipulators, stabilizers of a level of cryogenic liquids, transfer siphons, etc.), providing carrying out of low-temperature experiment without its stopping were executed. So, in 1975-1980 years the series of the inventions on the indicated positions has appeared.
It is necessary to stop on invention of USSR ¹981781 (1980), subject of which invention was a cryostat with a superconducting solenoid, earlier Medvedev department not released. Thus, among several types manufactured by Medvedev department of cryostats one more has appeared. By its characteristic differences from other cryostats with a superconducting solenoid of production DonPhTI ( Donetsk) and PhTILT (Kharkov), and also foreign corporations (at identical values of a received) magnetic field) were light weight owing to application of a welded body from lightaloy materials as against body from stainless steel, small cryoagent consumption and high stability of given temperature.
Due to the principles, included at constructing, of uniformity and agregation of the basic models of cryostats were ensured with every possible applications in scientific researches and their series has received the name UTRECS (from an abbreviation of the words Uniformed Temperature-Regulating Cryostat System).
This circumstance called new splash of popularity designed cryosystem. A stream of the orderings on them during 1981-1990 y.y. was so great, that in generated SCTB of physics inctruments with Experimental factory of Institute of physics AS of USSR it was necessary to open divisions for production of cryostats and temperature controllers, which production schedules provided discharge up to 36 units of production per one year. Cryosystems delivered in scientific organizations of all republics of USSR, and also in such countries UEP, as Poland, Bulgaria, GDR, SRCz. It was the star-shaped hour crostat production in Institute of physics, which was completed with the dissolving of USSR in 1991. Medvedev department, which has headed I.P.Zharkov has gone through hard hours: an amount both interior customers, and exterior because of the dissolving of a system UEP has falled sharply. Prime problems at this time were:
à) it was possible to make saving of collective of the designers, that due to the received state grants through link of State Committee of Ukraine on science and technique, due to which the new types of a cryogenic engineering designed: a temperature-controlled cryogenic little table for optical microscopes and temperature-controlled cryogenic attachments to electronic raster microscopes.
á) A heightening of a level and quality of designs for ensuring of a appierence of cryogenic production on the international capitalist market, which was won by such corporations as “ Oxford Instruments ” (England), “ Leybold Herraues ” (Germany), ” Cryo Industries Corp (USA).
The digital controller to this time any more did not meet the requirements the customers and time - to this time was widely applied microprocessor and computer equipment. Safronov together with other experts decided and this problem, namely to create a temperature controller of an intellectual (intelligent) type on a microprocessor basis with digital visualization of setted and flowing temperature and other parameters of process of regulation and possibility of controlof temperature from the digital computer. This ontroller on the characteristics did not yield to the best world analogs (see below-mentioned information).
Due to three circumstances: the high-precision costeffective cryostats both temperature controller of a modern type and low total cost of cryosystem managed to leave on the world market of cryoproduction During 1995- 2000 yy. tThe deliverings in the following countries were realized: Estonia (Institute of Physics of AS of Estonia,. Tartu 2 pcs.), Czechia (Institute of physics,. Prague - 2 pcs), Switzerland (University of. Zurich), Germany(Institute of radiochemistry,. Ìuelheim on Ruhr, Universities t.t. Regensburg, Marburg), France (Exploratory centre CEDEX), USA ( Montana St .university - 2 pcs) and Israel (Institute of solid state of Technion,. Hifa - 2 pcs.). In 2002-2004 yy. The deliverings of cryosystems were realized in Germany(Technical University of DArmstadt - 2 pcs) and in USA (Mississippi st. University) and Canada (Montreal st.University).
It is necessary to mark, that alongside with activity, directional on « survival of collective » and getting of the remedies for his development, the research work kept also, though its rates were not so high owing to above-stated reasons.
So, in 2003 year the system was created Unified Temperature-controlled Cryostat System, which ensures operation practically with anycryoagent type (except for Íå3 and its mixtures) with a highaccuracy of temperature control. And in 2004 the cryostat system for an optical microscope with temperature control in a ranget 40-800 K, which has not analogs in a world, was created.
It is necessary to mark, that basic ideas and thoughts À.F.Prihot'ko, V.S.Medvedev and V.L.Broude, included in constructions of cryostats, work and till to this day.
Developed solutions by their followers are embodied in cryostat systems produced as in Institute of physics of NAS of Ukraine and in Institute of a solid state physics (Chernogolovka). The Kiev cryostats with an abbreviation UNTRECS were awarded with Golden and Silver medals of USSRexhibition , have a Golden medal of the international Leipzig exhibition - fairs. They with success are operated in scientific organizations of such countries as USA, France, Germany, Israel, Czechia, Poland, etc. Therefore is possible uniquel to affirm, that matter À.F.Prihot'ko, v.S.Medvedev and V.L.Broude, lives and now.

.png)